Understanding Dog Body Language: Signs Of Fear, Aggression, And Play
Dog body language refers to the various ways dogs communicate through body postures, facial expressions, vocalizations, and behaviors. Understanding dog body language is important for pet parents and owners as it allows them to better interpret their dog’s emotions and needs. Recognizing key signs of fear, aggression, and play in a dog’s body language can help prevent misunderstandings and potential issues.
This article will provide an overview of some of the main signs of fear, aggression, and playfulness evident in dog body language. Identifying these cues allows owners to address potential problems, strengthen their bond with their dog, and ensure their pet’s health and happiness.
Ears
A dog’s ears are very expressive and can indicate their emotional state. When a dog is relaxed and happy, their ears will be in a natural position. For breeds with floppy ears, they will be loose and relaxed. For breeds with pointed ears, they will be up but relaxed, not stiff or upright.
Ears back indicate the dog is feeling fear or perceiving a threat. This is one of the most common signs of an anxious or frightened dog. When a dog pulls their ears back close to their head, it signals they are feeling defensive and want to avoid confrontation. This ear position exposes less of the inner ear and protects it during a potential conflict. It is the canine version of covering your ears.
Forward-pointed ears demonstrate interest, attention, and focus. When your dog perks up their ears and points them towards something, it means they are tuned into a sound or sight. Forward ears signify engagement and concentration as the dog hones in to gather more information.
According to Rover’s dog ear position chart, when your dog pins back their ears but still has a wagging tail, this likely means they feel anxious or conflicted. The wagging tail demonstrates friendliness, yet the flattened ears betray fear. Reading multiple dog body language cues together allows you to fully understand their complex emotions.
Eyes
A dog’s eyes can communicate many emotions and signals. Direct eye contact or staring can be a sign of aggression or a challenge in dogs. As the AKC explains, staring is considered threatening behavior in their wolf ancestors, so this often makes dogs uncomfortable (source). When a dog averts its gaze and avoids eye contact, this is a sign of avoidance or submission.
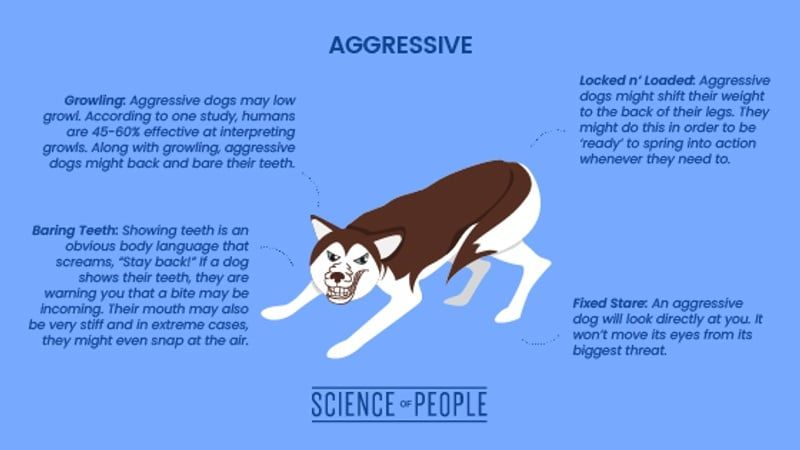
Dilated pupils can indicate fear or anxiety in dogs. As the pupils enlarge, more light enters which allows the dog to see better in a threat situation. Squinting eyes or showing the whites of the eyes is also seen in fearful dogs. However, squinting along with a tense posture is often a sign of aggression and discomfort with the situation.
While direct staring can be threatening, brief eye contact from dogs can also show confidence and bond with their human. As Rover explains, eye contact demonstrates charisma and comfort interacting with humans (source). So the meaning of a dog’s eye contact depends on the context of the rest of its body language.
Mouth
A dog’s mouth can reveal a lot about its emotional state. When a dog is relaxed and calm, its mouth will likely be open with the lips and jaws loose. This is a sign the dog feels comfortable with its surroundings and those around it. Panting can be a sign of stress or anxiety. The rapid breaths are the dog’s way of releasing nervous energy. On the other hand, lips pulled back to expose teeth is a warning sign of aggression. The dog is feeling threatened and defensive.
According to the Whole Dog Journal, ” commissure forward is often seen during play as well as during times of stress; commissure back is seen during states of aggression.” The positioning of the lips and gums communicates the dog’s mood.
Yawning when not tired is also believed to be a sign of stress in dogs. While small yawns may just indicate normal drowsiness, repeated wide yawns could mean the dog is feeling anxious or nervous.
Overall, a relaxed, open mouth signifies a calm, happy dog, while a tense, closed mouth with exposed teeth is a clear warning of aggression (source). Paying attention to subtle cues like lip position and panting can provide insight into how a dog is feeling.
Tail
A dog’s tail can communicate a lot about its emotional state. Here are some key things to look for:
Tail tucked between the hind legs signals fear, anxiety, or submission. This is one of the clearest signs of a frightened or worried dog (1).
A low, stiff tail wag often indicates uncertainty. The dog may be feeling insecure about a situation or person (2).
A broad, vigorous tail wag shows happiness and enthusiasm. This is the classic “happy dog” tail wag (1).
A slow wag with the tail lowered can signify attentiveness and interest. The dog is focused on something (2).
So pay close attention to your dog’s tail position and movement. It provides important clues into how they are feeling.
Sources:
(1) https://askvet.app/dog-tail-meaning/
(2) https://www.whole-dog-journal.com/behavior/dog-tail-language/
Hair
A dog’s hackles are the hairs that run along the dog’s spine. These hairs are attached to muscles under the skin which allow them to stand up, known as piloerection or raised hackles. When a dog’s hackles are raised it is communicating an emotional state, usually fear, aggression or excitement.
Raised hackles due to fear or aggression are a warning sign that the dog feels threatened and may lash out. The dog is trying to make itself look larger and more intimidating. This article explains how raised hackles indicate arousal and make the dog appear bigger to ward off perceived threats.
Raised hackles can also occur when a dog is extremely excited or happy. The hair stands up but the body language is loose and relaxed rather than stiff. According to this source, raised hackles during play displays the dog’s enthusiasm.
It’s important to look at the full context of a dog’s body language when its fur stands up. Stiff body, tense muscles, baring teeth likely signal fear or aggression. Relaxed open mouth, wagging tail indicate happiness and excitement. Understanding the nuances helps owners better read their dog’s emotional state.
Body
A dog’s body language can reveal a lot about its emotional state. Crouching with a lowered head and body often signals fear. The dog is trying to appear smaller and avoid perceived threats. Stiff, tense posture typically indicates aggression or anxiety. The dog is poised and ready to act. On the other hand, a play bow with the front legs stretched out and the back end up is an invitation to play. The dog is showing it wants to have fun.
According to the AKC article “How To Read Dog Body Language,” a crouched posture with a lowered head makes a dog appear smaller when it’s trying to avoid something stressful or frightening1. The Nylabone article “Dog Aggression vs. Playing” notes that a tense, stiff dog may show signs of fear aggression if it feels trapped or defensive2.
Vocalizations
Dogs communicate a lot through vocalizations. Some common vocalizations and their meanings are:
Growl – A growl is a warning sound that signals the dog is feeling threatened or annoyed. Growling is a defensive behavior meant to get whatever is causing the threat to back off. https://www.akc.org/expert-advice/advice/canine-communication-deciphering-different-dog-sounds/
Snarl – A snarl is an elevated growl that exposes the dog’s teeth. It signals immediate aggression and a readiness to attack if the threat doesn’t retreat. A snarl is often accompanied by a stiff body and an intense stare at the source of threat.
Whimper – Whimpering and whining are vocalizations dogs make when they are fearful, anxious, stressed or trying to communicate submissiveness. It’s a way for dogs to show they are not a threat and retreat from confrontation. https://www.fundacion-affinity.org/en/dogs-cats-and-people/i-have-pet/8-main-dog-sounds
Bark – Barking serves many purposes for dogs, but a common reason is to communicate alertness and warn about potential threats or intruders. It can also express excitement, loneliness, or affiliation. The tone and pitch of the bark provides clues to the dog’s emotional state.
Licking
Dogs will often lick their lips and nose when they are feeling stressed or anxious. Lip licking and nose licking can be a sign that the dog is uncomfortable with a situation and is trying to appease and avoid confrontation. This is an instinctual behavior that dogs use to communicate that they are not a threat. Excessive lip licking when seeing another dog or person can signify that the dog is fearful or unsure in that moment.
Dogs will also often lick the face and mouth of people or other dogs as a submissive gesture and to communicate friendliness. Face licking when greeting is thought to be a relic of puppyhood when puppies would lick the mouths of their mothers to get them to regurgitate food. Licking the faces and mouths of humans or other dogs is a sign that the dog respects the other being and wants to please them. It’s usually a sign of affection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding your dog’s body language is crucial for building a strong bond and ensuring their health and happiness. By recognizing key signs of fear, aggression, and playfulness, you can better meet their needs and avoid misunderstandings.
Some main signs of fear include ears back, tail tucked, lips tightened, and avoiding eye contact. Aggression signs include stiff body, tense muscles, staring, and baring teeth. Playfulness is shown through relaxed open mouth, wagging tail, and play bows.
Taking the time to learn your dog’s unique communication style will strengthen your relationship immensely. Paying attention to their body language allows you to address issues before they escalate and make sure your dog feels safe and understood.
With patience and practice, you can become fluent in “dog speak.” Your dog will be reassured knowing their person truly “gets” them. So observe your pup closely, socialize them extensively, and use your new understanding to build an unbreakable bond.